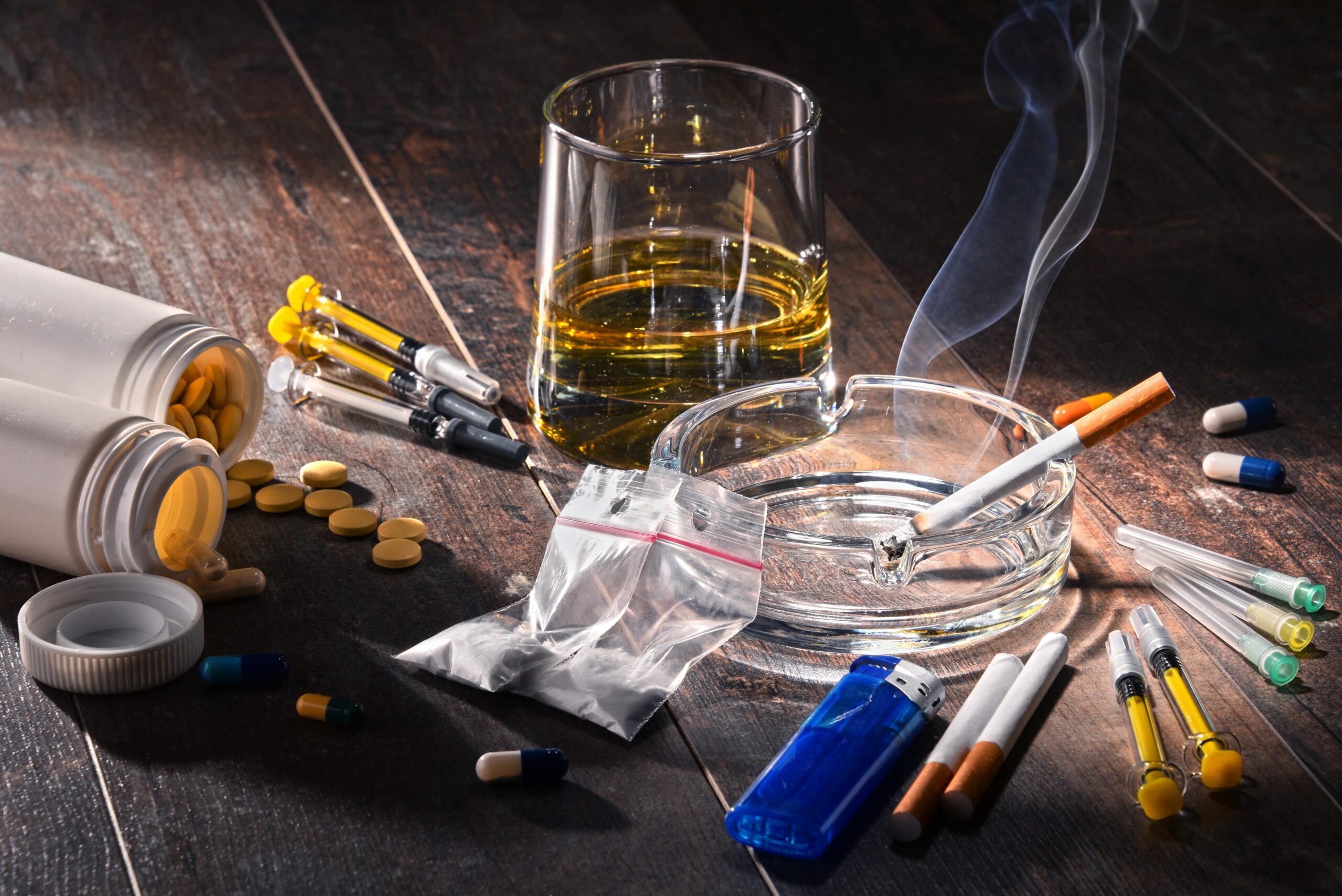
Curious about which drugs are the most addictive and why? Different substances have varying levels of addiction potential, largely due to their effects on the brain. By understanding drugs by addiction, we can better navigate the dangers they pose. Follow along as we dive into the types of addictive substances, their effects, and the most effective treatment options available.
Key Takeaways
Addictive substances are categorized into prescription medications, illegal drugs, and psychoactive substances, each with varying potential for addiction and health risks.
Substance Use Disorder (SUD) is a chronic condition characterized by compulsive substance use despite harmful consequences, necessitating comprehensive treatment approaches for recovery.
Preventing drug addiction requires a multifaceted strategy involving education, community engagement, and regulatory measures to create safer environments and reduce access to substances.
Understanding Drugs by Addiction: Types, Effects, and Treatment
Substances prone to abuse encompass a wide range, from legally prescribed medications and over-the-counter remedies to alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drugs. Sorting these substances into categories aids in the comprehension of their individual impacts on users and their potential for causing addiction. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has identified five distinct schedules of controlled substances that rank drugs according to their likelihood of misuse, underlining the importance of stringent regulations and diligent oversight.
By identifying how different drugs affect individuals both in the short-term and long-term, we can better understand just how addictive they might be along with what health risks they carry. Delving into various addictive agents, understanding immediate consequences as well as prolonged dangers, combined with assessing treatment alternatives, gives a holistic perspective necessary for addressing drug abuse effectively while fostering successful rehabilitation processes.
Introduction
Substance use disorders represent a significant challenge to health, often leading to extensive changes in brain function that can make cessation of drug use difficult for those desiring recovery. This problem pervades all demographics, including young individuals experimenting with drugs and older adults who may have been dealing with substance dependence over many years. It is essential to recognize that not everyone engaged in substance use will develop an addiction. The associated risks necessitate proactive efforts towards comprehension and intervention.
Key initiatives such as education and community outreach are crucial for mitigating the onset of drug addiction. Informing society about the detrimental impacts of substances can empower people to reject engagement with these dangerous items. Nevertheless, overcoming addiction transcends mere determination—it’s a medical condition demanding thorough treatment strategies alongside sustained support mechanisms. Acknowledgement of various addictive compounds, their adverse repercussions on well-being and behavior along with potential therapy options becomes pivotal when addressing this issue or aiding others afflicted by it.
Within this resource material lies an exploration into distinct classes of addictive agents detailing both acute and enduring effects they impart upon one’s health along with behaviors linked with consumption thereof. Examining intricacies surrounding disorders related to substance usage patterns are discussed herein too—amid outlining divergent remedial avenues accessible plus contemplating preventive methodologies aimed at curbing escalating instances tied to dependency phenomena.

Disorders related to substance use can be classified into three main types: those involving prescription medications, the utilization of illegal drugs, and the consumption of other psychoactive substances. These groups contain a variety of drugs with different levels of addiction potential and diverse impacts on both mental and physical health. Properly comprehending these distinctions is essential in order to identify dangers associated with substance use and implement effective interventions for such disorders.
Medications prescribed by healthcare professionals, including opioids as well as various stimulants, can sometimes lead to misuse despite being intended for legitimate medical reasons. Illicit drugs like heroin or cocaine are widely recognized for their strong tendency towards causing addiction. Legal psychoactive substances such as alcohol or nicotine also carry substantial risks regarding dependency.
Investigating these distinct categories thoroughly aids us in grasping how addictions develop while highlighting preventative strategies necessary to combat the onset of addictive behaviors tied to drug use.
Prescription Medications
Even though prescription drugs are meant for health-related use, they can often be misused and result in addiction. Pain relievers like oxycodone and morphine that belong to the opioid category are typically prescribed but have a high risk of leading to addiction. Likewise, stimulants such as methylphenidate, which is used in treating ADHD, carry a risk of misuse as well. These medications are regulated under the Controlled Substances Act. Act based on their likelihood of abuse juxtaposed with their medicinal value.
Engaging improperly with prescription medications may trigger severe health issues and pave the way for an addiction problem. It’s imperative to adhere strictly to medical guidance and recognize the danger inherent in these drugs’ usage. To combat such addictions effectively, treatments usually encompass a blend of counseling alongside medication that collectively addresses both psychological factors and physical dependence related to drug addiction.
Illegal Drugs
Illicit drugs, including heroin and cocaine, have a notorious reputation for their strong addictive properties and the significant harm they can inflict on individuals’ health. Their illegal status does not detract from the severity of addiction they cause, resulting in profound negative impacts both medically and socially. This emphasizes the critical need for robust regulations and effective programs dedicated to treatment.
The opioid epidemic serves as a stark example of drug addiction’s lethal consequences with approximately 90 Americans succumbing daily to an opioid overdose. Tackling the issue surrounding these illegal substances requires a comprehensive strategy that encompasses law enforcement efforts, public health policies, and ensuring that those battling with drug addiction have access to necessary treatment services.
Other Psychoactive Substances
The misuse of psychoactive substances, including socially accepted and legal ones like alcohol and nicotine, carries a substantial risk for addiction. Despite their legality, the harm they can cause when abused may parallel that of illegal drugs. Alcohol stands out as particularly addictive among these substances, with its overuse leading to numerous health complications and societal issues.
It’s important to recognize that the impact of substance abuse extends beyond individual users—it affects friends, family members, and even unborn children. Awareness about the dangers associated with misusing substances such as alcohol and nicotine is essential in preventing addiction and encouraging healthier lifestyle choices.
To alleviate the negative effects attributed to these addictive drugs requires a collective effort. Community support alongside educational initiatives are key elements in combating the pervasive issue of substance misuse.
Effects of Drug Addiction
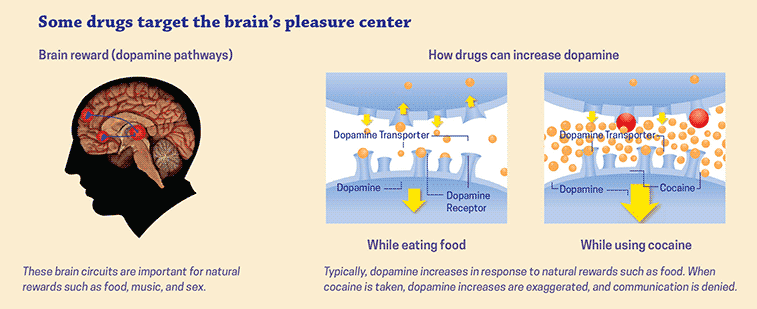
Addiction to drugs can profoundly influence both the physical and psychological aspects of a person, resulting in acute and prolonged negative outcomes. While varying types of drugs have distinct physiological effects, they lead to damaging health implications. Identifying these impacts is essential for detecting addiction indicators and pursuing appropriate intervention.
Immediate reactions stemming from drug use may manifest as alterations in mood, compromised decision-making ability, and feelings of intense pleasure. With continued substance consumption over time comes the potential for serious long-term medical complications, mental health conditions along with profound social and behavioral ramifications. A thorough examination of these consequences sheds light on the extensive toll that addiction takes on individuals as well as society at large.
Immediate Effects
The immediate impact of using drugs typically includes alterations in mood, a euphoric sensation, and diminished decision-making capabilities. This is largely due to an increase in dopamine within the brain’s reward system that not only triggers pleasure but also fosters an urge for Consumption of the substance. The specific outcomes can differ based on the drug involved, dosage taken, and any potential interactions with additional substances.
Although one might be enticed by the initial pleasurable high from drug use, this experience frequently comes with detrimental side effects like poor judgment and engaging in dangerous activities. These early stages often progress toward dependency and addiction problems, underscoring how critical it is to recognize the hazards associated with drug usage.
Long-term Health Consequences
Extended use of substances can culminate in serious, long-lasting health complications, encompassing harm to the liver and heart. Persistent drug abuse has the capacity to inflict permanent damage on essential organs, critically affecting a person’s general well-being. Mental health conditions like depression and anxiety may intensify with ongoing substance abuse.
As a result of enduring exposure to drugs, significant alterations occur within the brain that influence its operation and can give rise to persistent mental health disorders. Comprehending these protracted effects is crucial for acknowledging the comprehensive ramifications of addiction as well as highlighting the need for prompt intervention and treatment.
Social and Behavioral Impact
Addiction to drugs can result in individuals becoming socially withdrawn, distancing themselves from loved ones and neglecting their duties. Those suffering from addiction might avoid social engagements and fail to fulfill their roles at home or in the workplace. Such withdrawal has the potential to intensify the psychological issues related to addiction, deepening the cycle of detrimental behavior.
The intersection of social detachment and a disregard for obligations can markedly affect personal relationships as well as life satisfaction. It is essential to focus on these social and behavioral consequences when aiding individuals on their journey toward recovery, assisting them in constructing lives that are both healthy and rewarding.
Understanding Substance Use Disorder (SUD)
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a condition related to mental health, distinguished by a lack of control over substance consumption that leads to detrimental effects in an individual’s life. Prompt recognition of SUD is essential for starting appropriate treatment because it encompasses continual drug use even when faced with negative repercussions. Awareness and comprehension of the symptoms and risk factors tied to SUD can assist in pinpointing individuals at heightened risk and ensure they receive help swiftly.
Rather than being occasional substance usage, SUD represents a persistent state characterized by regular drug intake and an overpowering desire to obtain substances regardless of experiencing adverse outcomes. Examining the signs, contributing risks, and criteria needed for diagnosing SUD enables us to gain deeper insight into this intricate disorder as well as outline necessary measures for its management.
Symptoms of SUD
Withdrawal symptoms, escalating tolerance levels, and persistent pursuit of a drug are indicative of substance use disorder (SUD). Habitual substance users might experience physical signs such as stomach cramps or psychological effects like mental confusion upon ceasing intake due to the body’s adjustment to operating without the substance. An increased quantity of the drug is often required over time in order for individuals to attain their desired effect—a sign that they have developed a higher threshold for its impact.
The defining characteristic of SUD includes uncontrollable cravings and continued consumption even when faced with adverse outcomes. It is crucial to identify these patterns as symptomatic of SUD in order to properly diagnose this condition and begin effective treatment strategies aimed at managing withdrawal manifestations while fostering the journey towards recovery.
Risk Factors for SUD
Numerous factors elevate the risk of developing disorders associated with substance misuse, among them are an individual’s genetic makeup, their surrounding environment, and various developmental aspects. A predisposition inherited through genetics can heighten the probability that one may experience substance use disorders. Meanwhile, external elements like witnessing drug use or enduring stress significantly contribute as well.
Situations posing a high risk for individuals—like succumbing to peer pressure or navigating through life without adequate family support—can exacerbate the propensity for addiction and improper use of substances. Acknowledgment of these contributing factors is crucial in pinpointing those at a higher susceptibility to such disorders and deploying preventative strategies aimed at diminishing the chances of evolving into full-blown SUDs.
While encountering conditions linked to increased peril does not ensure development into substance-related issues definitively, they substantially boost the likelihood compared to those absent from such risks. By recognizing patterns related to escalated danger levels early on in exposure or usage cycles regarding drugs or other substances prone to misuse. Proactive intervention methods might be applied more effectively before deeper problems surface.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Assessment of Substance Use Disorder (SUD) entails examining the patterns of substance use and its consequential effect on everyday life activities. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), provides explicit criteria to diagnose SUD, emphasizing significant impairment or distress as a result of persistent drug use. Tools like AUDIT and CAGE questionnaires are frequently utilized for determining the extent of the disorder.
For an all-encompassing appraisal of SUD, it involves reviewing medical history, conducting psychological evaluations, and possibly performing substance testing. Healthcare providers might integrate clinical interviews with self-report surveys to gauge both occurrence and consequence of drug usage—crucial steps toward confirming a precise diagnosis that will guide effective treatment strategies for these disorders.
Treatment Options for Addiction
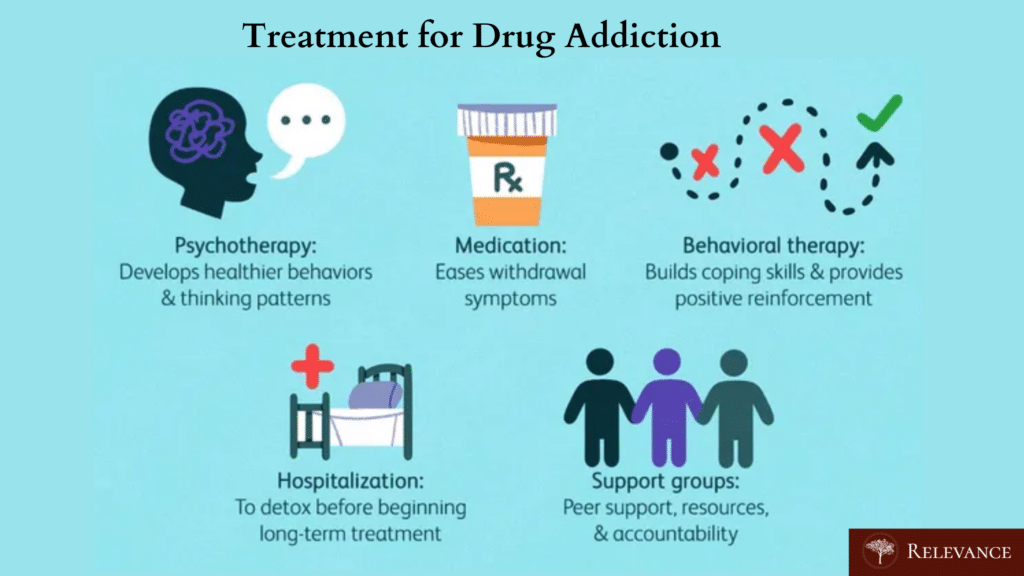
Disorders stemming from substance use can be effectively managed through a regimen of both medications and behavioral therapies. Studies have shown that individuals grappling with drug addiction can benefit from treatment that not only assists them in halting their drug use, but also supports them in maintaining sobriety and navigating the path to recovery. These treatments are most effective when they are personalized, addressing the evolving needs of those recovering by combining pharmacological approaches with therapeutic counseling to tackle both the physiological and emotional dimensions of substance dependence.
To combat these disorders adequately, an array of interventions is typically necessary, encompassing medication-assisted therapy (MAT), various forms of behavioral therapy, as well as residential care programs designed for intensive treatment engagement. Delving into these diverse methods offers valuable perspectives on aiding people who embark upon their journey toward recovery from substance addiction.
Behavioral Therapies
Behavioral therapies aim to alter detrimental behavior patterns linked to substance use by transforming negative thought processes and behaviors, thus equipping individuals with the necessary skills for handling stress and urges. These therapeutic approaches are frequently included in residential treatment plans that offer a supportive setting conducive to healing.
By tackling the psychological factors related to addiction, treatments utilizing behavioral therapies can notably enhance chances of successful recovery. To ensure an all-encompassing strategy towards overcoming addiction, these methods are typically integrated with additional forms of treatment modalities.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) employs a combination of pharmaceuticals alongside counseling and behavioral therapies, offering an integrated strategy to manage substance use disorders, particularly those related to opioid use. This approach is crucial for individuals grappling with addiction as it enhances the potential for successful recovery while diminishing relapse risks. Medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone are commonly used in MAT protocols to alleviate the cravings and withdrawal symptoms that accompany opioid dependence.
Legislation under Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act. The Act mandates parity in insurance coverage between substance use disorder services and other medical conditions. This ensures equal access to essential mental health service administration for affected individuals. By incorporating MAT into their regimen, healthcare practitioners can deliver more effective and enduring treatment solutions for patients confronting the challenges of addiction.
Residential Treatment Programs
Residential treatment facilities offer a controlled environment conducive to addressing the challenges of recovery. These inpatient programs cater specifically to those with acute cases of addiction, providing an all-encompassing level of care aimed at tackling both physical and mental aspects associated with substance use disorders. The continual provision of medical assistance and therapeutic guidance within these residential settings is vital for patients grappling with intricate issues related to substance use.
To optimize individual patient outcomes, residential treatment protocols frequently integrate medication-assisted interventions alongside behavioral therapies. Such personalized regimens ensure that each person battling addiction receives optimal care and backing throughout their journey towards recovery.
Preventing Drug Addiction
Addressing drug addiction requires a multifaceted strategy that encompasses education, community engagement, and enforcement of regulations. It is essential to acknowledge the hazards linked with substance use for safety and reduction of harm. Initiatives centered on education and outreach are crucial in heightening awareness and educating people about the repercussions associated with substance misuse. A combination of these educational initiatives with active community participation fosters an environment conducive to discouraging the misuse of drugs.
The implementation of policies and legal constraints also has a critical function in curbing drug addiction. Rules that restrict availability to drugs coupled with laws enforcing age restrictions can markedly lower the danger posed by substances, particularly among younger individuals. By tackling these diverse elements collectively, efforts can be made towards fostering a society adept at averting addiction related to substance use while providing support for those embarking on recovery journeys.
Education and Outreach
Education helps people understand the risks of drug use, making it a cornerstone of prevention efforts. Prevention programs can involve families, schools, communities, and the media. These initiatives help in preventing drug use and addiction. Research shows that combining educational efforts and community involvement significantly enhances the prevention of drug abuse.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) emphasizes the importance of education and outreach in preventing substance misuse. Raising awareness through education empowers individuals to make informed decisions and avoid the pitfalls of addiction.
Community-based programs are particularly effective in reaching diverse populations and addressing local needs.
Protective Factors
Robust family ties play a crucial role in safeguarding against substance abuse. The presence of strong connections with family members and active participation in various activities are critical defensive elements that assist youth in steering clear of substance misuse. Involvement in extracurricular pursuits acts as a barrier, diminishing the chances of engaging in drug use.
Firm relationships within the family, peer encouragement, and engagement with extracurricular activities stand out as vital protective factors that help prevent drug use. By nurturing these factors, we can establish an environment conducive to supporting individuals to withstand the lure of substances and cultivate healthy behaviors along with effective coping strategies.
Policy and Regulation
Implementing policies that enforce age restrictions for purchasing substances can effectively diminish young people’s access to them. Curtailing the promotion of alcohol and tobacco through regulations is also instrumental in lowering rates of substance use among teenagers. Establishing and upholding these measures promotes a more secure environment that mitigates the dangers associated with substance misuse.
Support from organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is crucial for community-level initiatives aimed at restricting substance accessibility, which can lead to substantial decreases in susceptibility to substance misuse. Sound policy-making coupled with stringent regulation plays a vital role in an all-encompassing approach designed to combat drug addiction while safeguarding public health.
Summary
Addiction to drugs is a multifaceted health issue that disrupts both cognitive functions and behavioral patterns, making the path to recovery arduous yet achievable. It’s imperative to gain insight into the various classes of addictive substances, their impact on individuals, and the assortment of remedial options at hand in order to effectively confront substance use disorders. This spans from prescribed medications and illicit drug use to mind-altering agents like alcohol and nicotine, each necessitating specific prevention strategies and treatment modalities.
Early identification of symptoms and understanding the risk factors associated with substance use disorder are key elements for providing prompt assistance and backing for those afflicted. A range of successful treatments exist—including therapeutic interventions focused on behavior modification, treatments augmented by medications, as well as inpatient programs—which illuminate paths toward rehabilitation. Engaging in preventative measures such as public education initiatives, community participation activities, along with implementing regulatory policies, are pivotal steps towards fostering a more wholesome community. By uniting our efforts, we can tackle this pervasive issue head-on—supporting affected individuals down their road towards regaining control over their lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most addictive prescription medications?
Prescription medications, including opioids such as oxycodone and stimulants like methylphenidate, carry a high risk of addiction. It is essential to exercise careful supervision over their use due to the considerable potential for misuse.
How does drug addiction affect the brain?
Addiction to drugs profoundly impacts the brain’s reward system, causing shifts in mood and compulsive actions due to heightened dopamine levels. This disruption can drastically affect one’s ability to make decisions and exercise self-control.
What are the symptoms of substance use disorder?
Substance use disorder is characterized by symptoms such as withdrawal symptoms, increased tolerance, and compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
Recognizing these signs is crucial for seeking appropriate help.
What treatments are available for opioid use disorder?
Treatment for opioid use disorder includes a comprehensive approach that incorporates medication-assisted treatment (MAT), such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone. This is combined with behavioral therapies and participation in residential treatment programs to form effective treatments.
Participation in these types of treatments can greatly improve the chances of successful recovery from opioid use disorder.
How can drug addiction be prevented?
Drug addiction can be effectively prevented through education, community engagement, and strengthening protective factors such as family connections while also enforcing policies that limit access to harmful substances.
These strategies collectively create a supportive environment that reduces the risk of addiction.
Dr. Mitchell G. Cohen is a board-certified Internal Medicine specialist with over 34 years of experience in patient-centered healthcare. A graduate of Hahnemann University School of Medicine, Dr. Cohen completed his internship at the University Health Center of Pittsburgh, where he gained invaluable hands-on experience. He is also a certified addiction specialist, holding membership with the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM).
Currently based in Nashua, NH, Dr. Cohen is affiliated with Saint Joseph Hospital, where he provides comprehensive care focusing on both internal medicine and addiction treatment. His expertise includes prevention, diagnosis, and management of adult diseases, as well as specialized care for individuals facing substance use disorders.
Dr. Cohen is committed to fostering open communication, ensuring his patients are fully informed and empowered to make confident decisions about their health and treatment options.

MD Mitchell Grant Cohen
Dr. Mitchell G. Cohen is a board-certified Internal Medicine specialist with over 34 years of experience in patient-centered healthcare. A graduate of Hahnemann University School of Medicine, Dr. Cohen completed his internship at the University Health Center of Pittsburgh, where he gained invaluable hands-on experience. He is also a certified addiction specialist, holding membership with the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM).
Currently based in Nashua, NH, Dr. Cohen is affiliated with Saint Joseph Hospital, where he provides comprehensive care focusing on both internal medicine and addiction treatment. His expertise includes prevention, diagnosis, and management of adult diseases, as well as specialized care for individuals facing substance use disorders.
Dr. Cohen is committed to fostering open communication, ensuring his patients are fully informed and empowered to make confident decisions about their health and treatment options.







